

Internet of Things and insurance: How the technology affects the industry
Initially viewed as a domestic pet that automates the functioning of home appliances and smart systems without people’s intervention, the Internet of Things (IoT) today has made a robust advent into other spheres of our lives. Technology-savvy entrepreneurs and organizations employ IoT apps and solutions in various use cases across multiple industries – from healthcare, automotive, and logistics to agriculture, manufacturing, and retail.
IoT ideas are quickly and inevitably disrupting the insurance markets. Today, various companies already gather data from connected devices to simplify claims management and deliver more personalized services. Further, the role of IoT will only grow, forcing underwriters to evolve to remain competitive.
If you represent this industry, you may wonder how to catch the wave. DICEUS will guide you through all the basics, demonstrate significant IoT benefits, and reveal the top challenges for IoT in insurance. Of course, thanks to our professional background in insurance combined with advanced technologies, we can help design safe and profitable IoT-driven insurance software.
The number of connected devices is growing rapidly
First things first, we should understand IoT clearly. The IoT refers to interconnected elements: sensors, computing programs, machines, items, and even people. All of them can exchange data directly, forming a new type of network that doesn’t require a human operator to control everything.
It’s possible that you don’t trust in the bright future of IoT. That’s typical for businesses. But it’s also dangerous to refuse to accept modern trends. According to Statista, since 2019, the number of connected devices will get triple the growth by 2025. Of course, it affects the insurance market, as well. People use these gadgets to equip their homes and cars, generating valuable data for your business.
IoT devices increase in number way faster than we do. Three essential factors support this growth:
- Connectedness. People tend to use innovations and connected solutions mainly. They appreciate the convenience brought by these technologies.
- Data. Sensors regularly collect new information about customers and the world. This trend enables the growth of big data strategies vital for modern businesses.
- Power. According to Moore’s law, IoT gadgets (as well as other computing systems) can increase their power exponentially. This is true for the number of devices, too.
Planning to upgrade your system? Consider insurance claims management software development services.
The Internet of Things enables new opportunities for insurers who are ready for changes. Thanks to next-gen data processing principles, this technology allows getting market insights unattainable earlier. Innovations open ways for new business models. Moving further, let’s look at these strategies, as well as the benefits enabled by IoT nowadays.
Internet of Things in insurance today
Regarding the current situation in the insurance industry, we want to refer to Ben Luckett, Managing Director at Aviva. He says that markets are quickly changing now. Previous generations considered insurance as an inevitable evil, outdated, and blinkered. But technologies change everything, even in traditional ecosystems.
Mr. Luckett insists that the growth of IoT with the idea of ubiquitous connected sensors increased the amount and quality of data – a core resource for any Internet of Things insurance team. As a result, these changes drive significant shifts in business models. While there are different approaches to evolution, Aviva expert focuses on two Internet of Things trends in the insurance industry:
- From historical to real-time data. Insurers have to learn how to process almost unstoppable streams of data. By understanding real-time data, they can deliver more personalized products that lead to win-win interactions between businesses and clients.
- From responsive to predictive services. Thanks to real-time streams, insurers also should be able to understand customer needs better. From preventing road accidents to diagnosing illnesses early, predictive services can boost mutual satisfaction.
Keeping these points in mind, let’s talk about the advantages that IoT strategies bring to the insurance industry and the challenges to overcome. It’s crucial to know both the positive and negative sides so you will be able to develop your business correctly. This information can also help you get more tailored programs for your company.
If you want to learn more about modern insurance, check out the guide in our blog. It unveils the hottest trends in insurance software development for the next two years.
Benefits of IoT products for insurance
In a nutshell, digital-driven operations allow underwriters to cut costs and maximize revenue. Indeed, they must implement innovations properly to get these benefits. Here are the key advantages of implementing IoT in insurance:

- Generate extra revenue. The exact causes of this benefit include next-gen direct customer interaction with more personalized offers, the development of new services based on advanced insights, and optimization of prices tailored to demand.
- Reduce unnecessary expenses. Examples include increased efficiency relying on automated prevention methods, improved safety with new standards like automated real-time reactions, and sensor-based analytics to prevent fraud.
- Optimize risk prediction and prevention. Thanks to IoT solutions for insurance, companies can adopt a preventative approach and predict the occurrence of issues. IoT sensors and devices can issue alarms about malfunctions to forestall property damage and, consequently, lower the number of claims.
- Streamline claims processing. If an accident occurs and a claim is registered, IoT solutions enable insurers to process it faster and more efficiently. They also automatically notify employees about the incident, facilitating the claim management pipeline.
- Enhance fraud detection. By spotting irregularities and anomalies, IoT systems provide insights into the nature of insurance-related operations and events, red-flagging those that seem fraudulent. Then, personnel can investigate them more closely, ruling out the chances of overpaying in such cases and minimizing the company’s financial loss.
- Tailor policies. By helping track client behavior, IoT devices allow for a personalized approach to underwriting and policy pricing. For example, car insurance companies have direct data from vehicles, such as speed and driving behavior. Thus, they can better evaluate the risks of accidents and provide more tailored policies. The same is true for healthcare, where wearables help monitor patients’ parameters 24/7.
- Increase customer experience. The personalization and customization of policies and streamlining of client-facing workflows (like auto-filling claim form fields) the IoT technology ushers in result in happy and loyal customers whose time and efforts are saved in this way.
- Augment home safety. IoT devices benefit not only insurance companies but their clientele as well. People whose dwellings are equipped with such systems enjoy a greater level of safety since IoT sensors alert insurers if something goes wrong and they interfere to prevent accidents and emergencies.
Apart from costs and income, parties that use IoT devices for insurance can manage risks. For example, car insurance companies have direct data from vehicles, e.g., speed and driving behavior. Thus, they can evaluate the risks of accidents better and provide more tailored policies. The same applies to healthcare, where wearables help monitor patients’ parameters 24/7.
Top challenges for IoT in insurance
Still, the implementation of IoT in insurance isn’t a cakewalk. It requires a lot of time and resources to prepare, get the required software, and transform operations. We don’t see the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things in the insurance industry because of several critical challenges. It’s vital to overcome them to start building new-age insurance. Here they are:
- Resistance to change. Historically, the insurance industry has always been among the most conservative domains. Transformation drivers often struggle to bring home to all stakeholders the necessity and indeed the inevitability of embracing disruptive technologies and create a universal buy-in concerning making IoT-powered solutions a pivotal element of the insurance digital environment.
- Clear-cut strategy. All random and irregular attempts at harnessing IoT solutions for insurance workflows are doomed to failure if they don’t rely on a well-thought-out and meticulous implementation roadmap developed by a competent IT vendor with an in-depth understanding of the industry’s nuts and bolts.
- Integration of IoT devices. IoT products bring the most value when they work in harmony with other digital products. However, synchronizing their functioning and standardizing their interoperability protocols require high-profile expertise and (very often) specialized middleware to ensure compatibility of all elements within an IoT ecosystem.
- Business models. IoT can disrupt traditional ways of doing business. Together with benefits, insurers will face a slight revenue decrease in the beginning. Thus, they have to find new services based on IoT and focus on clients, not companies.
- Data management. Even existing businesses often fail to process key data they receive. With the rise of real-time streams, this task will become more complicated. To deal with the issue, insurers have to invest in new enterprise strategies and tools.
- Data ownership. As for now, there is no answer to the problem of data ownership. Customers think that they should control data recorded by their sensors. Insurers believe that they also have rights. This issue has yet to be resolved.
- Data security. Of course, with the growing number of connected gadgets that collect valuable info, we will see more frauds and hackers. For insurers, this process marks the importance of perfect cybersecurity systems that can protect users.
- Regulations. Challenges related to data ownership, privacy, and processing result in a heated debate. Today, governments can regulate this industry, so let’s remember about standards and laws related to IoT.
These challenges prevent many insurers from diving into innovations. But it’s still possible to transform your business. With the professional help of domain experts and talented software developers, digital/IoT evolution goes much smoother.
Top connected ecosystems for insurers
Moving further, we also want to share with you some insights unveiled by McKinsey researchers. Based on the emerging Internet of Things trend in the insurance industry, digital disruptions, and the overall popularity of insurance services, it’s possible to name four major ecosystems that hide an enormous potential. They differ by maturity, dynamics, customers, competitors, and regulatory challenges. Let’s see how the Internet of Things insurance companies operate!
1. Connected health
This is a well-known industry that is rising thanks to wearables as the main IoT application for life insurance. Personal IoT gadgets help to monitor patient conditions constantly by delivering priceless insights.
Doctors can now check way larger data packages, so they can identify diseases faster and prescribe more effective treatments. Thanks to tools like Verisense by Shimmer, people can get a small gadget and predict severe illnesses like cancer before they become incurable.
Thanks to personal and corporate IoT systems, insurers get better vision, too. They can identify health-related risks to offer the demanded products. In combination with smart household solutions, connected health gadgets also open a whole new industry – ambient assisted living. It helps aged people in their everyday lives. Underwriters deliver bundles of tailored services and even can act as healthcare curators who drive hospital-at-home interactions.
Considering custom solutions? Learn more about insurance mobile app development.
2. Connected vehicles
Today, cars are boxes full of electronic sensors. These gadgets monitor almost everything, from speed to pressure to wear of various details. If a driver has personal devices like smartphones or wearables, he/she also becomes a part of this local system. A-and, you got it. All these sensors produce telematics data. This information can be gathered by insurers in real time to optimize claims management, handle risks, and offer better products for each given customer.
It’s highly likely that with the rise of connected cars, insurance companies will face a decline in claim frequency with the simultaneous increase of claim sums. But this will lead to a revenue decrease, as well. That’s why insurance businesses have to think about new sources already. Applications of IoT in car insurance include work with workshops, service add-ons, risk management services, and other intelligent systems like parking and so on.
3. Connected construction/smart real estate
This fiercely competitive field is fraught with various dangers that require consideration by insurance agencies performing risk assessment and damage evaluation. IoT systems connect construction sites, machinery, and people to monitor situations in real-time, collect data, and analyze land stability, water level (for littoral plots), wind intensity, and other parameters that factor in while determining policy pricing.
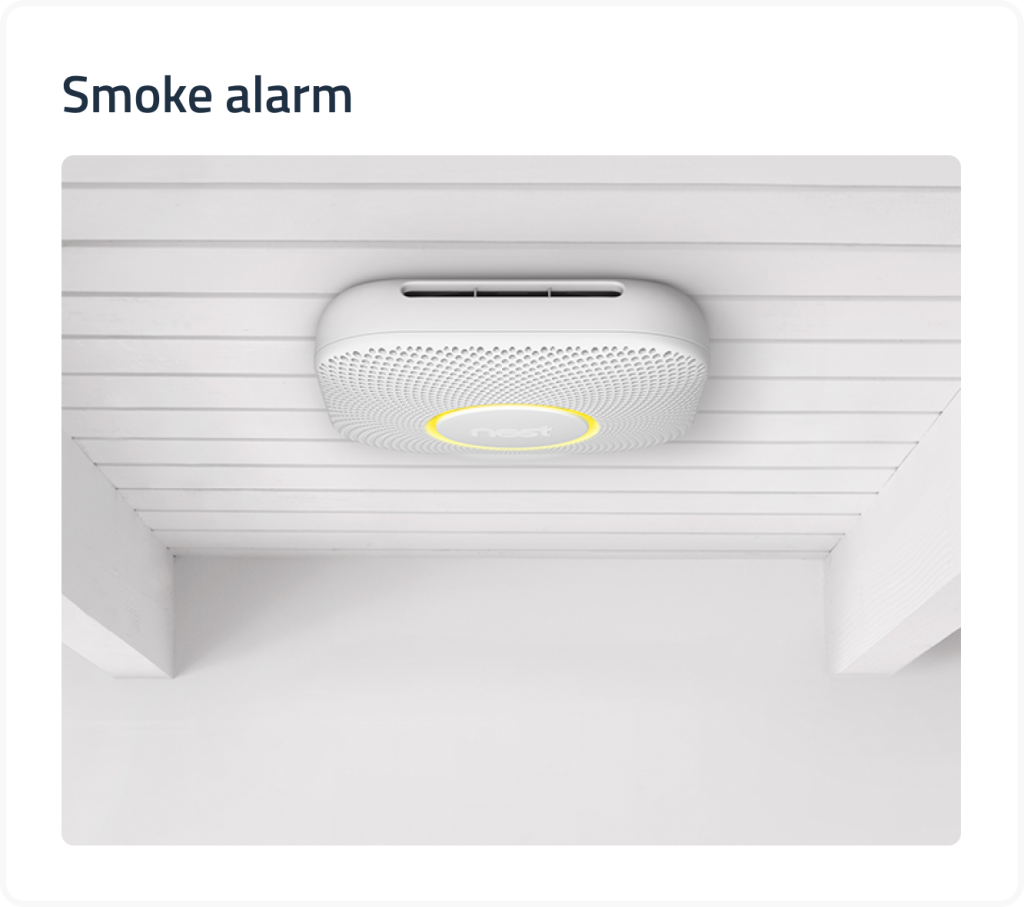

In existing residential and commercial buildings, IoT infrastructure helps detect harmful substances in the air (smoke, CO2, and the like), mold on surfaces, and other adverse instances that may cause problems both for residents and insurers alike.
Also, IoT devices can be mounted on construction workers, warning them (and the insurance company) that they are approaching some dangerous location and thus preventing fraudulent claims concerning accidents in the workplace.
Insurance risk management software development services can help you improve risk assessment processes.
4. Commercial lines
Apart from personal interactions, insurers can always work with businesses. This B2B approach will undoubtedly flourish thanks to IoT. The catch is that corporations are interested in all-in-one solutions or policies that protect companies all the way along the supply chain. Here are the most notable parts of this journey:
- Planning. It’s especially valuable for innovative digital-oriented firms. For them, IoT-powered underwriters can offer next-gen cybersecurity services.
- Manufacturing. Various sensors can be installed in factories and plants. They predict accidents, help to get data to optimize processes, and boost worker experience.
- Warehousing. As well, insurers can process info from sensors in storage. They will help to assess risks and set better prices for corporate insurance.
- Sales. Again, IoT can enable better risk management. For example, capital-to-risk matching provides for the trading of insurance securities and transferring risks.
- Distribution. Fleet management is essential for all companies that deliver goods. In this case, insurance ideas for connected cars work fine.
Planning to add some features to your system? Learn more about the insurance agency management software development.
5. Smart homes
This ecosystem is probably the most famous. Even before this notion appeared, residential dwellings and industrial buildings were equipped with fire suppression systems that reacted to rising temperature or smoke within and turned on sprinklers to extinguish the starting conflagration.
In recent years, software and hardware developers such as Google, Samsung, Amazon, and Apple have presented dozens of smart home solutions for the mass market. Today, almost every citizen can purchase a smart camera, a leakbot, or even smart appliances. All these gadgets are integrated thanks to cores—virtual assistants or smart home hubs that control other devices.
Insurers benefit significantly from this growing industry. They can collect data from thousands of households, process it, and identify risks for each property. Based on this analysis, they create custom policies. Many insurers sell integrated products via smart assistants. They also create new services, such as improved protection from leaks or greater convenience for owners of smart homes.
6. Drones
IoT devices and sensors don’t have to be static. They can be mounted on drones whose high-resolution cameras are a second-to-none instrument for registering what is happening in real-time in hard-to-reach places. The pictures and videos these flying nose-pokers supply provide valuable data that helps insurance agencies in risk evaluation, damage assessment, and other pipeline operations, thus enhancing efficiency, accelerating claims processing, and reducing associated costs.
7. Agriculture
Modern agriculture has long ago turned from a manual and physically demanding job into a machine-powered and essentially digitalized business. IoT technology contributes much to the mechanization of the sector, helping high-tech savvy farmers determine crop health, soil state, moisture level, and other critical parameters. When these are inadequate, IoT systems automatically switch on the irrigation or allow people to make data-driven decisions concerning further actions.
When supplemented with weather forecasts, environment information (such as temperature and humidity), and reports on the presence of hazardous conditions and substances (for instance, toxic fumes, smoke, radiation, mold, etc.), IoT-generated data can be used by insurers as well. Leveraging the entire complex of these records, they assess risks and climate-caused damage to the future harvest and tailor their insurance policies accordingly.
8. Industrial IoT
Today, IIoT is all the rage across such verticals as logistics, aviation, manufacturing, and more. Various sensors are installed in factories and plants, where they predict accidents, help to get data to optimize processes, and boost worker experience. Smart data provided by them enables the personnel to monitor machinery performance, identify maintenance issues, and keep the workplace safe.
Insurers utilize the same data to offer customized premiums to organizations and individual employees in which IIoT data is used as a pricing and risk benchmark. Moreover, when accidents are forestalled before they occur, insurance companies avoid financial losses resulting from hefty disbursements.
How can you maximize the value IoT systems bring to your business?
How to improve your IoT-driven services
To start a successful IoT product insurance project, it’s not enough to get a reliable solution and connect to sensors. There are a few steps required to make the best insurance IoT system:
- Define customer needs with exact application areas.
- Ensure that the systems are scalable and can work with Big Data.
- Increase the delivery speed regardless of the services’ complexity.
- Look at long-term strategies with global reach.
- Set strategic partnerships as early as possible.
Carrie Lonze from Accenture says that modern insurers should think about a new approach – the Internet of Thinking. According to insights, unique insurance ecosystems will be based on edge architecture that provides for data processing and analysis via sensors, not central servers. The main reason is the growing amount of data.
Also, Lonze also notes that some companies have made significant progress in automated processing thanks to edge computing. For example, a startup called Aerobotics uses satellite imagery to predict crop health. More traditional groups like Allianz France use constant monitoring of construction sites to predict various risks.
Move ahead with DICEUS
Whether you’re only thinking about the Internet of Things insurance ideas or already have a plan, don’t hesitate to contact us. We have rich experience in this field, with a few notable solutions developed, i.e., Benefitnet and Insubiz. Our experts can help with all stages of software development, from the first consultation to proof of concept projects to launch and support. We care about innovations and like to be involved in game-changing activities. Let’s work together!
Frequently asked questions
What are the impacts of IoT on the insurance industry?
When insurance companies embrace IoT technology on a large scale, they streamline claims processing, underwriting, and other shop floor operations, enhance fraud detection and prevention, reduce OPEX, create additional revenue channels, usher in a personalized approach to individual clients, and boost the customer experience of policyholders.
How does IoT impact claims management in the insurance industry?
As a rule, submitting and processing a claim is a lengthy procedure with a lot of red tape that policyholders have to go through, often in stressful conditions. IoT, as a data-driven technology, accelerates claims processing, minimizes fraud instances, reduces waiting time for customers, allows them to track the progress of their claim, and facilitates disbursements if the claim is found valid.
What challenges does the insurance industry face in adopting IoT technology?
To successfully implement IoT tools in the insurance pipeline, organizations should address such issues as the conservatism of multiple stakeholders, absence of clearly-defined strategy, disruption of traditional methods, integration of IoT devices with other elements of the professional infrastructure, data management, ownership, and security, regulatory compliance, and more.
How can insurance companies address privacy concerns related to IoT data collection?
Conventionally, IoT devices come with subpar cyber protection, where legacy firmware doesn’t rely on strong security protocols. To mitigate penetration threats, you should secure network configuration, leverage data encryption techniques, apply stringent user authentication methods, and foster consumer security awareness and education. The latter includes promoting responsible IoT utilization, educating users on privacy risks, and advocating for accountability and transparency.
How can insurers leverage IoT data for product innovation?
With IoT data up their sleeve, insurers can abandon traditional approaches that are based on historical data and backward-looking risk studies. IoT devices supply them with real-time insights that can be used to establish premium pricing and policy terms. Besides, relying on IoT-generated data, insurance agencies can personalize their offers and upselling recommendations, tailoring their marketing campaigns to address the unique needs of each customer.





