Hospital mobile app development: Benefits and key features
Modern hospitals are principal healthcare hubs where patients obtain a great range of medical services. Moving in the wake of the across-the-board digitalization that penetrates an ever-growing number of fields, these healthcare facilities go to all lengths to make their services available to as wide a target audience as possible and guarantee a superb customer experience for medical services consumers.
Mobile apps for hospitals are second-to-none instruments that can address both mentioned challenges and take the quality of services a clinic provides to patients to a new level. This article explains the assets of hospital app development, enumerates the features a hospital application should contain, and dives into the nitty-gritty of hospital app SDLC.
Let’s begin with the perks these mHealth products can bring to their users and the healthcare organization that launches them.
Benefits of custom hospital apps
As a vetted hospital app development company, DICEUS realizes the advantages of hospital apps for medical service providers and their clients.
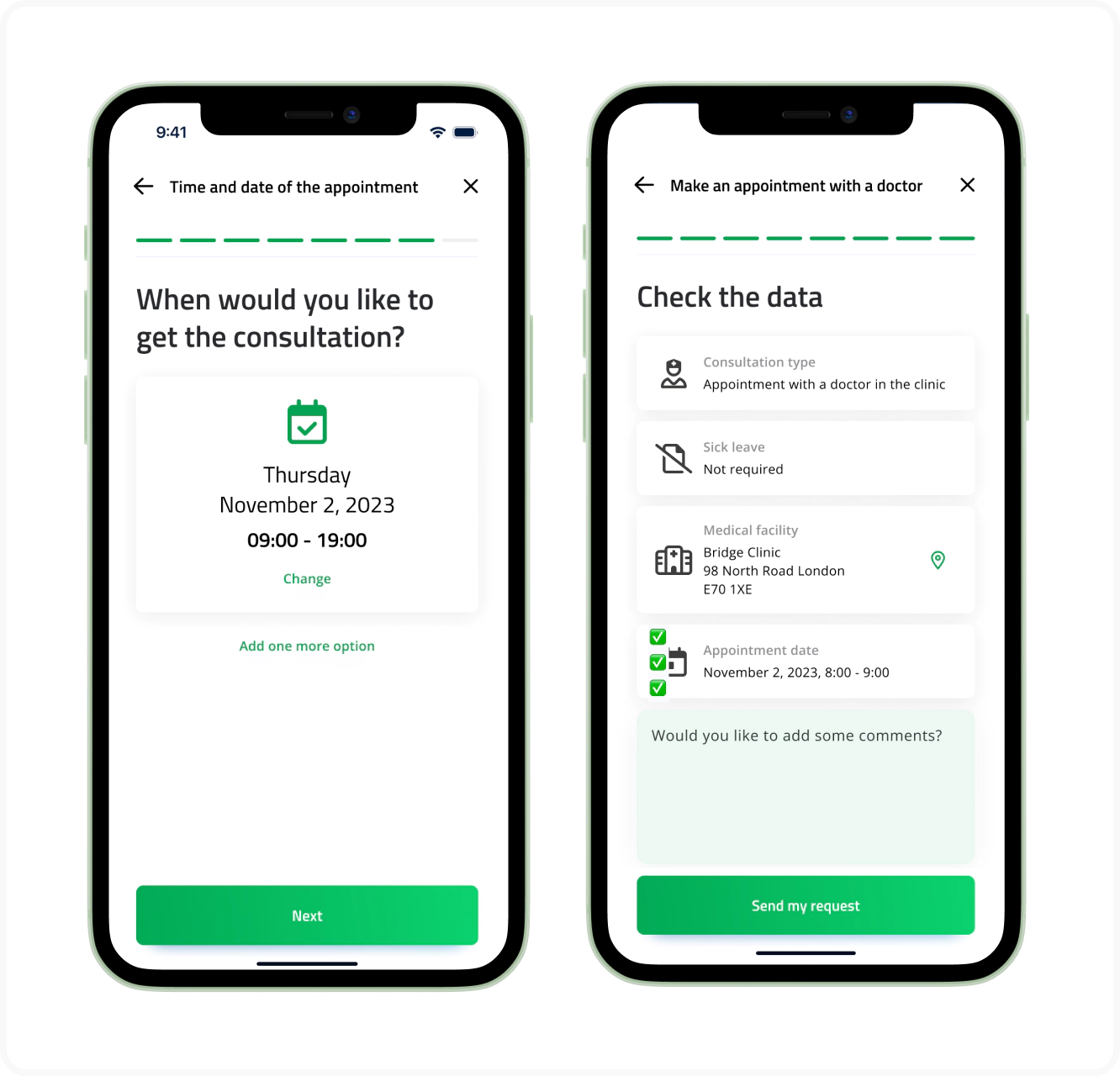
Benefits for patients
- Increased availability and inclusivity of medical services. With a stable internet connection and a smartphone in their hand, people can obtain instant help or consultation from a specialist, no matter where either of them is. Such telemedicine opportunities are vital for underserved strata of the population whose mobility is limited (for instance, bedridden patients or physically challenged seniors).
- Time-saving. In the healthcare industry, a delay in getting medical assistance may be fatal. With a mobile app at their fingertips, people can receive urgent pre-doctor care on short notice and win critical minutes that otherwise would cost them health or even life.
- Cost-efficiency. Traveling to the hospital entails expenditures on fuel, fare, food, etc., especially if a person has to cover a great distance to get there. And if it is some minor ailment or a routine consultation, such trips seem a sheer waste of money. A hospital app allows them to stay at home and get the same level of services.
- Hassle-free appointment booking. When you do need a meeting with a doctor, a special AI-powered chatbot that most hospital apps are equipped with will make appointment scheduling a breeze.
- Monitoring opportunities. Hospital apps are integrated into a single ecosystem with a network of IoT healthcare products, enabling people to track their condition 24/7. Their critical indices (such as pulse rate, blood pressure, glucose level, etc.) are transmitted to the physician’s computer in real-time so that they can intervene if something goes wrong and requires urgent action.
- Foolproof bill payment. The paperwork routine associated with medical expenditures and insurance coverage is now history. Utilizing the special functionality of their hospital app, people can take a few taps on their phone and pay the bill online. Or they can leverage a dedicated health insurance app for the same purpose.
Want to integrate telehealth into your hospital software?
Check out our telemedicine software development services.
Benefits for hospitals
- Accessibility. Doctors need to monitor sick people, especially discharged or home-care outpatients. A hospital app allows them to do this without leaving their premises and leverages its telehealth capabilities to provide medical services from their workstations.
- Excluding infection spread. When a lot of people pack a hospital’s waiting room, the chances of an infection being transmitted among them increase manifold. Turning a waiting room into a virtual venue existing only in a hospital app helps avoid such consequences or at least mitigate them.
- Better time management. Hospital apps are powerful tools for regulating patient flows, minimizing missed appointments and cancellations, and augmenting the scheduling pipeline. As a result, hospital personnel’s efficiency and productivity grow exponentially while workload distribution inadequacies are kept to a minimum.
- Cost-efficiency. Hospital apps allow organizations to delegate many tasks to artificial intelligence. By employing a range of high-tech app features, healthcare providers can cut down on their support personnel costs and minimize expenditure allocation for keeping patients’ dossiers in paper format.
- Less red tape. Having most documents in e-format has one more upside. Hospital apps can be augmented with automation tools that drastically streamline the notorious paperwork handling that takes up a fair share of a physician’s working hours.
- Access to EHR. The round-the-clock availability of a patient’s personal and medical data in Electronic Health Records allows clinicians to receive a 360-degree view of their clients and boost diagnosing, treatment plan selection, medication prescription, and more.
- Collaboration between specialists. Apps for hospitals serve as a communication channel not only between doctors and patients but between physicians as well. Medical experts can team up with remote colleagues to discuss difficult cases or dubious diagnoses and arrive at an optimal solution for the problem they face.
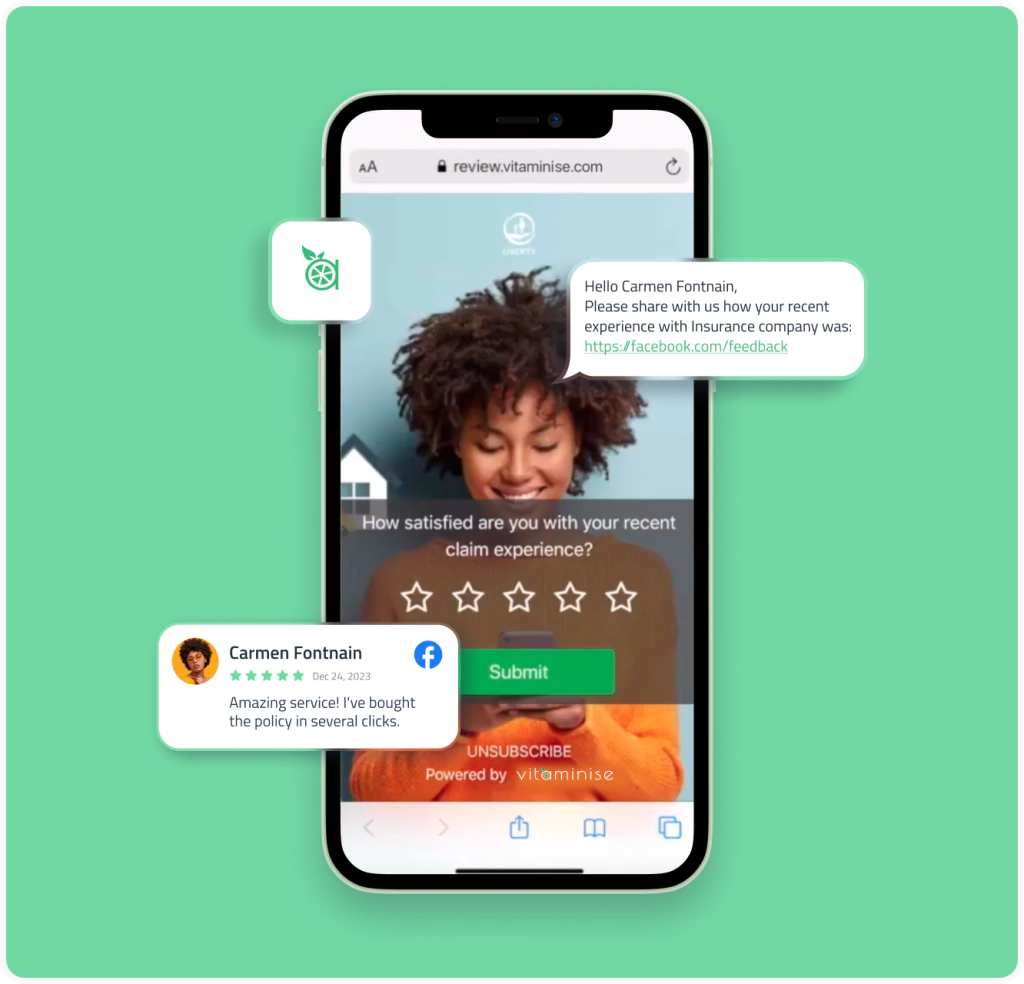
- Collecting feedback. To improve their shop floor processes, healthcare providers need to know what patients think about their quality. Hospital apps can be geared toward collecting opinions of medical services consumers that can be later used as actionable insights in fine-tuning a hospital’s pipeline, closing efficiency loopholes, and improving the functioning of departments that underperform.
- Advancing brand reputation. If your hospital has a custom app, it will manifest a high level of digital awareness in your facility. The app showcases your organization to the best advantage as a high-tech-savvy player in the niche that stands out among the competitors and keeps abreast of the latest achievements in the IT realm.
- Fostering patient loyalty. By leveraging personalization opportunities and customer engagement tools employed in app design (interactive elements, rewards, bonuses, and other gamification techniques honed for creating a satisfying user experience), your hospital app caters to the needs of a wide user audience and encourages them to stay with your organization and even recommend it to their friends and family.
- Promoting your company. Mobile apps are robust marketing tools. Thanks to them, hospitals can administer campaigns, extend special offers, share news, and make other strategic moves to advertise the organization, attract customers, and turn one-time patients into loyal clients.
You can maximize a hospital app’s value to patients and doctors by filling it with the right capabilities.
Features of hospital apps for patients
For such a competent hospital application development vendor as DICEUS, it is clear that the term “hospital app,” in fact, encompasses two standalone products – one geared for patients and the other for medical facility personnel. Alternatively, you may say that it is one solution with two user interfaces. Each of them contains a different roster of features.
A hospital app for patients includes:
- Registration. It is a bread-and-butter functionality of most service apps, but it has certain peculiarities for healthcare software. First and foremost, it must be super secure. Under HIPAA stipulations, hospital apps should rely on multifactor (preferably biometric) authentication and authorization techniques to prevent leakage of sensitive personal data. Secondly, users should be able to upload files from third parties (for instance, social media or EHR systems).
- Home page. After completing the registration, the patient comes here as to a departure point of the user journey in their navigation about the solution.
- Profile. Here, users enter both demographic and medical data about them (date of birth, geographic and electronic address, physical parameters such as height and weight, images, insurance policy number, etc.). To streamline all activities managed via the app, the profile should be synchronized with hospital records.
- EHR access. Patients should be able to view their complete medical history, test results, records concerning their visits to specialists, and other documentation. It goes without saying that this gateway should also be protected while data funneled through it should be encrypted.
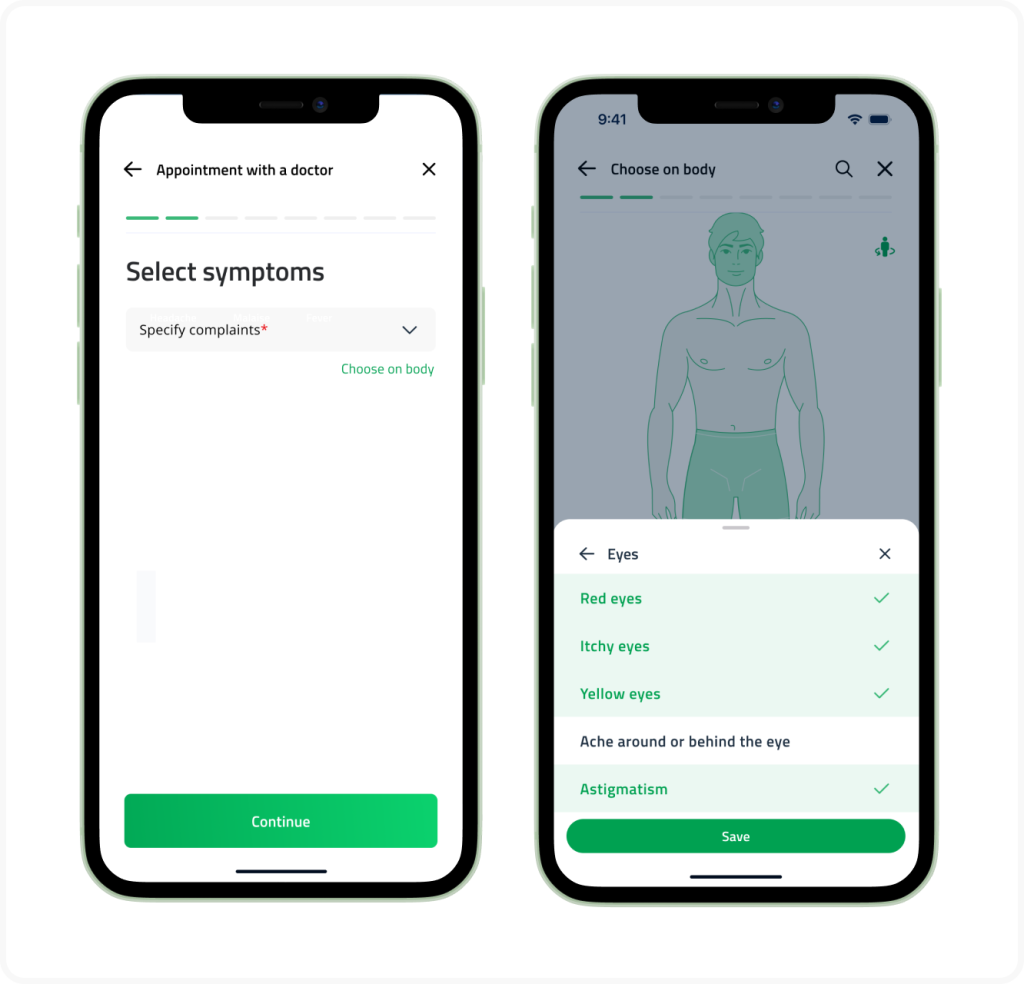
- Symptom checker. It is one of the novel capabilities that has quickly come to the top of the list of most sought-after healthcare app features. This self-service tool harnesses NLP algorithms to accept a patient’s complaints and symptom descriptions, state the preliminary diagnosis, and recommend what specialist to see for further action.
- Search capabilities. This feature should be equipped with a system of filters that allows patients to choose a clinician according to their qualifications, specialty, and experience. To help people with their choices, they should be given an opportunity to read reviews from previous clients who have used the doctor’s services before.
- Appointment scheduling. When the user knows what physician they would like to cooperate with, they should be taken to the doctor’s schedule with appointment slots (the calendar feature is a must here). After the appointment has been booked and confirmed by the clinic, the patient should receive an approval notification.
- Prescription management. Thanks to this functionality, people can view their current medications, read dosage instructions and relevant warnings, and request prescription refills. The necessary condition for including this feature in the app is its integration with pharmacy systems.
- Communication media. The hospital app should enable live interaction between stakeholders in the treatment process. Video calls and live chats, as the core telehealth capabilities, provide real-time communication where patients and doctors can discuss symptoms, diagnoses, and therapy to be applied in this particular case.
- Push notifications. Such messages keep patients updated about oncoming appointments, routine checkup visits to a specialist, prescription renewals, and more. They also can be configured to remind the user to take medications on time.
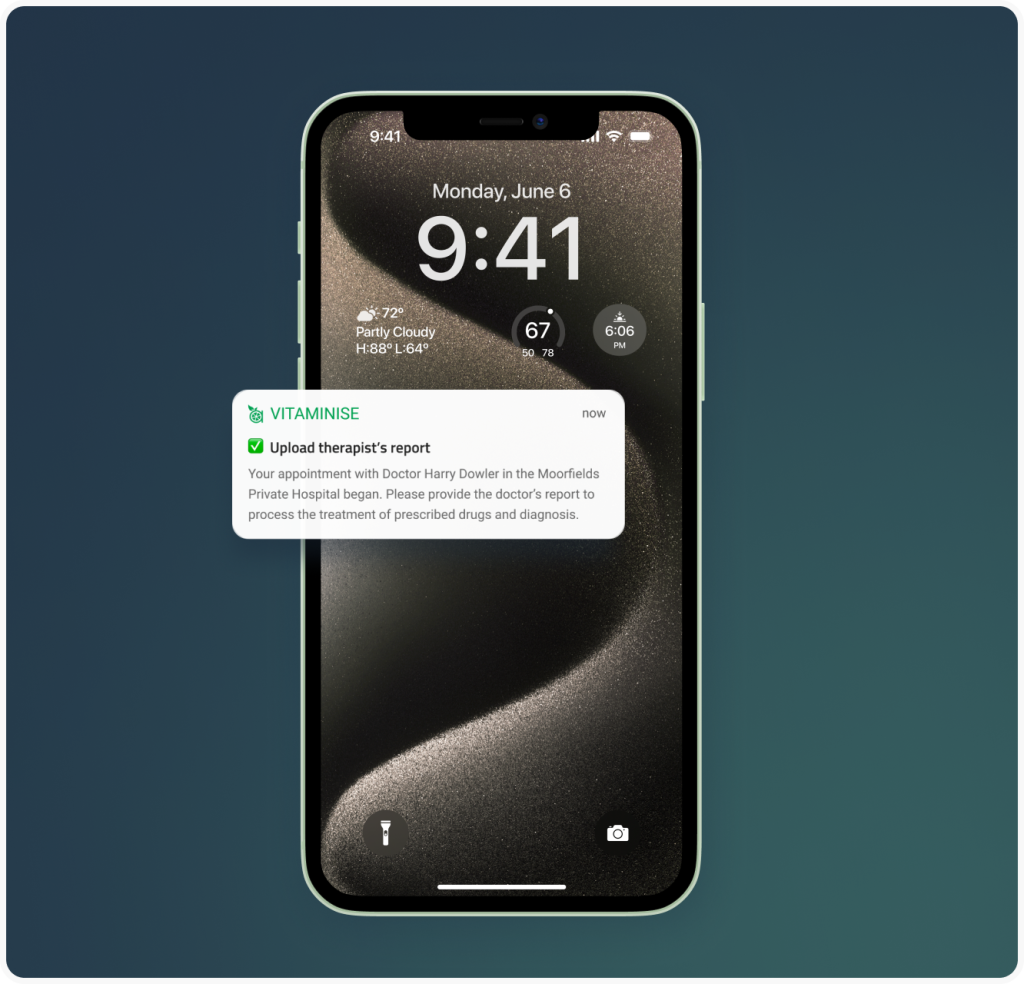
- Payment gateways. Hospital apps should be integrated with major payment systems so that people can choose the one they are comfortable with to pay for medical services.
- Integration with wearables. People should be able to use the app to track their health metrics (for instance, blood pressure or heart rate) supplied by various wearable devices. In this way, hospital apps will become a unified platform where critical data from various gizmos monitoring individual health areas is gathered.
- Voice control. Since many patients have locomotive or visual impairments, including this feature will make the app accessible to a wider user audience.
- Virtual assistants and chatbots. Thanks to them, patients will be able to receive personalized advice and assistance in their queries. To maximize their value to the customers, these tools should embrace cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Contact information and emergency services. Healthcare services consumers should know who to contact in case of emergency. Apps should enable one-tap helpline dialing and be integrated with a geolocation mechanism to direct a person to the nearest emergency facility.
Features of apps relevant to hospital staff
To make the app a pivotal element of a hospital’s IT ecosystem catering to healthcare personnel, it should be provided with such features:
- Doctor’s profile. It should contain the basic information about each physician (education, certification, experience, specialization, etc.) as well as hospital pipeline details, such as internal ratings and working shifts.
- Access to EHR. Correct diagnosis and prescribing treatment are impossible without clinicians’ 24/7 access to patients’ dossiers kept in EHR databanks.
- Appointment management. This pipeline optimization tool is pivotal for efficient workload planning and avoiding personnel burnout.
- Interaction channels. These are identical for patients and doctors since both leverage chats and video calls to establish professional communication. The only difference between them is the feature enabling doctors to record patients’ online visits. This way, specialists can review the sessions at their convenience and confirm or reconsider their previous judgments.
- Data sharing. Such mechanisms usually complement communication tools and are chiefly used for doctor-to-doctor interaction. Utilizing them, clinicians can exchange lab test results, X-ray or MRT images, and other data to involve colleagues in diagnosing and choosing the treatment method.
- E-prescriptions. Doctors use this feature to generate and send prescriptions to patients, thus avoiding manual errors and reducing paperwork.
- Pharmacy database. By browsing it, physicians can learn about various drugs, their ingredients, application areas, side effects, and dosage limitations. Thus, they will be able to select the one that suits every treatment plan to a tee.
When you decide what features your future hospital app will contain, you can get down to building it hammer and tongs.
Need a custom healthcare software solution? Check out our telemedicine app development services and other hospital management software development services you might be interested in.
A step-by-step guide to hospital application development
Over a dozen years of our presence in the healthcare mobile app development niche, we at DICEUS have devised the following roadmap for creating such products.
Step 1. Requirements analysis
Also known as the discovery phase, this stage lays the foundation for developing any software. During it, our experts meet the customer’s representatives to discuss all the details concerning the future product. We learn about the project’s business goals, its target audience, the app’s focus, the roster of features the customer would like to see in it, and the project’s expected timeframe.
Step 2. Tech stack selection
The feature list and the platform of the app-to-be (Android, iOS, or cross-platform) condition the choice of technologies to be used in SDLC. An important element of technical requirements for the project is the state of the current IT environment the customer relies on. Having such information on our table, we determine frameworks, programming languages, and novel know-how (AI, ML, IoT) necessary to complete the project as well as its integration needs.
Need help with tech stack selection?
Check out our healthcare software development services
Step 3. Determining the team composition
In accordance with the skills the tech stack requires, we identify the specialists for the project team. To build a medium-size hospital app, the IT team needs a project manager, a front-end developer, two back-end developers, a UI/UX designer, and a QA expert. In case the scope of the project is greater, any of these positions will be reinforced.
Step 4. Prototyping
First, we build a proof of concept to see whether the app model we have drafted holds water. If it does, we transform it into a clickable prototype showcasing the product’s UI.
Step 5. Building an MVP
The Minimum Viable Product is the first fully functional app version containing the solution’s core functionalities. After the trial audience has tested it, we collect the feedback, analyze it, and introduce corrections if necessary.
Step 6. Coding
This is the longest stage. During it, we utilize the approved MVP as a skeleton to be upgraded and amplified on the way to receiving a full-fledged app. As a rule, we kick off by building the app’s backlog, which lists its system logic, functionalities, and product architecture. Having the backlog as a point of reference, we design the app’s UI and initiate back-end coding when our developers create the features, deal with their dependencies, and implement integrations.
Step 7. QA and testing
The finished product must undergo a series of manual and automated tests. The QA team conducts unit, stress, performance, functionality, usability, compatibility, acceptance, compliance, and other kinds of tests to ensure the app behaves according to expectations and no bugs hamper its functioning.
Experiencing a lack of technical expertise and skills?
Connect with a professional team to address your project challenges.
Step 8. Deployment
Once the app’s operation is found safe and efficient, we deploy the product, and it goes live.
Step 9. Support and maintenance
DICEUS is a responsible IT company, so we never call it a day after the app is delivered for the customer to use. We continue cooperating with the partner to monitor the first stages of the product’s operation, introduce minor improvements, fix issues if they arise, and offer advisory assistance concerning any aspects of the app’s functioning.
As you see, building a robust and seamlessly performing hospital app that satisfies all customer requirements is a tough row to hoe. That is why you will need a competent IT vendor with in-depth experience in the domain to deliver a high-end product within time and budget. The qualified and certified developers of DICEUS possess the necessary expertise to build a hospital app of any scope and complexity. Drop us a line to obtain a top-notch hospital app that will impress users with smooth operation and sleek design.
Key takeaways
To keep abreast of the latest high-tech achievements, healthcare organizations embrace digitalization on a large scale. Hospital apps can become essential elements of their IT ecosystem and usher in numerous benefits both for medical personnel and patients. They act as a 24/7 available instrument for providing and obtaining medical services, drastically streamlining and facilitating a healthcare institution’s workflow. Hospital apps can bring maximum value to their users if they are equipped with relevant capabilities and are created by high-profile software professionals according to a straightforward SDLC roadmap.
FAQ
What features are commonly included in hospital apps?
The choice of features is conditioned by the app’s target audience. If it is a patient app, it usually contains such capabilities as registration, profile, doctor search, symptom checker, appointment scheduling, communication media, push notifications, chatbot support, and payment gateways. The must-have features for a hospital’s personnel are doctors’ profiles, EHR access, appointment management, communication tools, data sharing, e-prescriptions, and a pharmacy database.
How can hospital apps benefit patients?
By installing a hospital app, patients get 24/7 access to high-quality medical services and constant health monitoring opportunities. They can save time and money on appointment booking, bill payment, health insurance claim processing, and other elements of the healthcare service provider pipeline.
How do hospital apps improve operational efficiency for healthcare providers?
When medical institutions make a hospital app an integral part of their IT ecosystem, they boost their service accessibility, improve personnel time management, cut down on OPEX, minimize red tape routine, enhance collaboration between specialists, and obtain an excellent promotion tool for improving their brand’s reputation and fostering patient loyalty.
What role do telemedicine features play in hospital apps?
Thanks to them, patients can arrange virtual visits to the specialist they need. People can obtain valuable advice and timely help without leaving their premises, thus reducing the risk of spreading contagious diseases. Besides, telemedicine capabilities allow doctors from remote locations to hold joint sessions to discuss diagnoses and prescribe treatment methods.
Are hospital apps customizable based on the specific needs of a healthcare institution?
The essence of custom hospital app development services is building a bespoke product tailored to the needs of a specific healthcare provider. Organizations that commission such a product select the features and capabilities they and their clientele will use in their workflows and integrate the app into their IT infrastructure, thus maximizing its value to all stakeholders.